03 .WorkManager多进程支持
WorkManager 多进程
WorkManager 对多进程的支持
在 WorkManager 2.5 中,我们使多进程应用程序可以更轻松地访问指定进程中运行的特定 WorkManager 实例。
在 WorkManager 2.6 中,我们更进一步添加了对 Workers 在任何进程中运行的支持,并允许 Workers 绑定到特定进程。多进程支持对于需要在多个进程中运行 Workers 的应用程序特别有用。
从 WorkManager 2.6 开始,您可以使用 RemoteListenableWorker 或 RemoteCoroutineWorker 将 Worker 绑定到特定进程。如果您使用 kotlin 来实现 Worker,请使用 RemoteCoroutineWorker,而其他情况则使用 RemoteListenableWorker。
RemoteCoroutineWorker 实现起来和 CoroutineWorker 很相像,但不用覆写 doWork,而是覆写 doRemoteWork,并在生成 WorkRequest 时将 ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME 和 ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME 两个参数传入 InputData 来将其绑定到特定进程。
引入多进程好处
配置 WorkManager 并使用 RemoteWorkManager 调度作业时,您的工作会在多进程应用中得到更快速、更可靠的管理。这是因为 SQLite 争用 情况会大大减少 (因为我们不再依赖于以文件为基础的锁定),且不再需要跨进程的作业协调,因为您的应用仅会在您指定的进程中运行单个 WorkManager 实例。
WorkManager 多进程方案
1、官方的 WorkManager 的 multiprocess 方案
- 官方提供的 WorkManager 多进程方案
- 通过继承实现 RemoteWorker
- 这种方案 WorkManager 的广播和服务都是在主进程,也就是说周期性唤起在主进程,然后通过绑定服务 RemoteService 到指定的进程,将 Worker 运行在该进程中
2、更彻底的 WorkManager 的多进程方案
- 自己维护一套 WorkManager 源码
- 将 WorkManager 的广播和服务都定义在子进程,这样周期性唤起和 Worker 都运行在子进程中
- 这样维护成本高一点
官方 WorkManager 多进程方案(multiprocess 方案)
引入支持 WorkManager 多进程的库
implementation "androidx.work:work-multiprocess:$work_version"
自定义 WorkManager 初始化
移除 WorkManager 的默认初始化
默认情况下,WorkManager 通过 AppStartup 初始化,在名为 WorkManagerInitializer 的单独提供程序中初始化
<provider
android:name="androidx.startup.InitializationProvider"
android:authorities="${applicationId}.androidx-startup"
android:exported="false"
tools:node="merge" >
<meta-data
android:name="androidx.work.WorkManagerInitializer"
android:value="androidx.startup" />
</provider>
崩溃:
如果 WorkManager 开启了多进程,又没有移除默认的初始化,会崩溃:
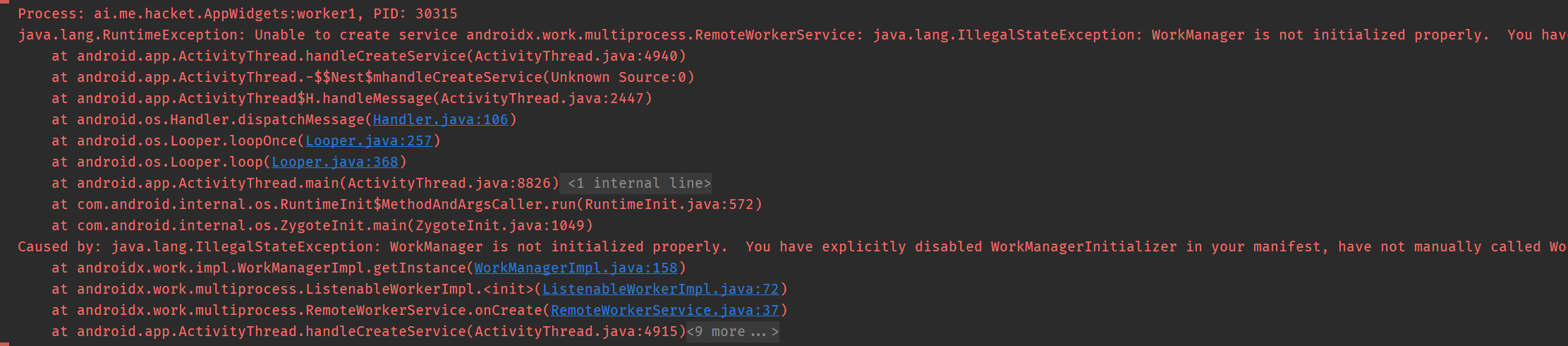
原因:
默认 InitializationProvider 是在主进程初始化,而在多进程是没有初始化的,所以会崩溃
解决:
要开启 WorkManager 对多进程的支持,需要在多进程手动初始化。
方式 1:Application 初始化
在 manifest 文件中禁用 WorkManagerInitializer provider 程序,并将默认初始化在 Application.onCreate 。
<provider
android:name="androidx.startup.InitializationProvider"
android:authorities="${applicationId}.androidx-startup"
tools:node="remove" />
定义 RemoteWorkService 运行的进程:
<service
android:name="androidx.work.multiprocess.RemoteWorkerService"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1" />
Application 中自定义初始化:
class TestApplication : Application(), Configuration.Provider {
override fun getWorkManagerConfiguration() =
Configuration.Builder()
.setDefaultProcessName("com.example.background.multiprocess")
.setMinimumLoggingLevel(android.util.Log.DEBUG)
.build()
}
- 您需要传递完全限定的进程名称作为
setDefaultProcessName的参数,该名称由您的应用包名称,后跟英文冒号和主机的进程名称组成,例如com.example:remote。看了源码setDefaultProcessName没有什么实际作用,更多的是用来输出 log - 使用
work-multiprocess时,您需要使用RemoteWorkManager(而非WorkManager) 来管理您的工作请求。RemoteWorkManager 将始终使用指定的进程将您的工作加入队列。这可确保您不会在调用进程中意外初始化新的 WorkManager。进程中调度程序也会在指定的同一进程中运行。 - 这种方式是不指定进程初始化的,每个进程都会初始化
方式 2:自定义一个 WorkManagerInitializer
- 将
InitializationProvider指定进程:workmanager
<provider
android:name="androidx.startup.InitializationProvider"
android:authorities="${applicationId}.androidx-startup"
android:process=":workmanager"
android:exported="false"
tools:node="merge">
<!-- 移除默认的WorkManagerInitializer -->
<meta-data
android:name="androidx.work.WorkManagerInitializer"
android:value="androidx.startup"
tools:node="remove" />
<!-- 添加自定义的WorkManagerInitializer -->
<meta-data
android:name="me.hacket.assistant.samples.google.architecture.appstartup.WorkManagerInitializer"
android:value="androidx.startup"
tools:node="merge" />
</provider>
- 自定义 WorkManagerInitializer
class WorkManagerInitializer : Initializer<Any> {
override fun create(context: Context) {
val configuration = Configuration.Builder().build()
// WorkManager.initialize(context, configuration) // WorkManager is already initialized. Did you try to initialize it manually without disabling WorkManagerInitializer? See WorkManager#initialize(Context, Configuration) or the class level Javadoc for more information.
// Log.d("hacket.WorkManager", "WorkManagerInitializer create: ")
return WorkManager.initialize(
context,
MyWorkManagerConfigurationProvider().workManagerConfiguration
)
}
override fun dependencies(): List<Class<out Initializer<*>>> {
// No dependencies on other libraries.
return emptyList()
}
}
class MyWorkManagerConfigurationProvider : Configuration.Provider {
override fun getWorkManagerConfiguration(): Configuration {
return Configuration.Builder()
.setMinimumLoggingLevel(android.util.Log.INFO)
.setWorkerFactory(RenameWorkerFactory())
// .setExecutor()
// .setTaskExecutor()
// .setInputMergerFactory()
// .setMaxSchedulerLimit()
// .setDefaultProcessName()
// .setInitializationExceptionHandler()
// .setRunnableScheduler()
// .setWorkerFactory()
.build()
}
}
替换为 ExampleRemoteListenableWorker/RemoteCoroutineWorker
将原有的 CoroutineWorker 改成 ExampleRemoteListenableWorker/RemoteCoroutineWorker
RemoteCoroutineWorker
- 自定义
RemoteCoroutineWorker
class ExampleRemoteCoroutineWorker(context: Context, parameters: WorkerParameters) :
RemoteCoroutineWorker(context, parameters) {
override suspend fun doRemoteWork(): Result {
Log.i(
TAG,
"Starting ExampleRemoteCoroutineWorker, process=${
getCurrentProcessName(applicationContext)
}"
)
delay(5000L)
val s:String? = null
s!!.toString()
Log.w(
TAG,
"End ExampleRemoteCoroutineWorker, thread=${Thread.currentThread().name}, process=${
getCurrentProcessName(applicationContext)
}"
)
// Do some work here
return Result.success()
}
}
- 配置
RemoteWorkerService,指定进程,也可以自定义了RemoteWorkerService
<service
android:name="androidx.work.multiprocess.RemoteWorkerService"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1" />
- 子进程中要初始化 WorkManager 的配置,特别是自定义了 WorkManager 的情况下
- 配置 WorkRequest,和普通的不同,增加了
RemoteListenableWorker.ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME和RemoteListenableWorker.ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME- ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME 直接获取
context.packageName - ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME 要绑定的
RemoteWorkerService
- ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME 直接获取
private fun buildOneTimeWorkRemoteWorkRequest(
componentName: ComponentName, listenableWorkerClass: Class<out ListenableWorker>
): OneTimeWorkRequest {
// ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME and ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME are used to determine the service
// that a Worker binds to. By specifying these parameters, we can designate the process a
// Worker runs in.
val data: Data = Data.Builder()
.putString(RemoteListenableWorker.ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME, componentName.packageName)
.putString(RemoteListenableWorker.ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME, componentName.className)
.build()
return OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(listenableWorkerClass)
.setInputData(data)
.build()
}
val serviceName = RemoteWorkerService::class.java.name
val componentName = ComponentName(this, serviceName)
val oneTimeWorkRequest = buildOneTimeWorkRemoteWorkRequest(
componentName,
ExampleRemoteCoroutineWorker::class.java
)
workManager?.enqueue(oneTimeWorkRequest)
自定义 RemoteWorkerService
- 自定义 RemoteWorkerService
/**
* This class is to demonstrate tagging a worker with a different service in order to bind separate
* workers to different Services.
*
* See [RemoteCoroutineWorker] and [RemoteListenableWorker] for more
* information about how the arguments [ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME] and [ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME] are used
* to determine the service that a Worker can bind to.
*/
class RemoteWorkerService2 : RemoteWorkerService()
- 清单注册
<service
android:name=".workmanager.multiprocess.RemoteWorkerService2"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker2" />
- 绑定:
val serviceName = RemoteWorkerService2::class.java.name
val componentName = ComponentName(applicationContext.packageName, serviceName)
val oneTimeWorkRequest = buildOneTimeWorkRemoteWorkRequest(
componentName,
ExampleRemoteListenableWorker::class.java
)
workManager?.enqueue(oneTimeWorkRequest)
ExampleRemoteListenableWorker 多进程
/**
* Example of implementing a RemoteListenableWorker. This worker simply returns Success.
* <p>
* Use RemoteListenableWorker if your worker is implemented in Java, otherwise use
* RemoteCoroutineWorker if your worker is implemented in Kotlin.
*/
public class ExampleRemoteListenableWorker extends RemoteListenableWorker {
private static final String TAG = "Worker.ListenableWorker";
public ExampleRemoteListenableWorker(Context appContext, WorkerParameters workerParams) {
super(appContext, workerParams);
}
@Override
public ListenableFuture<Result> startRemoteWork() {
return CallbackToFutureAdapter.getFuture(completer -> {
Log.i(TAG, "Starting ExampleRemoteListenableWorker");
// Do some work here.
return completer.set(Result.success());
});
}
}
Ref
小组件多进程和自定义 WorkManager 多进程方案
WorkManager 唤醒和 doWorker() 都在子进程
如何查看进程存活
# Windows
adb shell "ps |grep ai.me.hacket"
# Mac
adb shell ps | grep ai.me.hacket
如何覆盖 WorkManager 自带的服务和广播?
基于 workermanager-runtime-v2.7.1
<!--覆盖官方WorkManager-->
<service
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.SystemAlarmService"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="@bool/enable_system_alarm_service_default"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n" />
<service
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemjob.SystemJobService"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="@bool/enable_system_job_service_default"
android:exported="true"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_JOB_SERVICE"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n" />
<service
android:name="androidx.work.impl.foreground.SystemForegroundService"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="@bool/enable_system_foreground_service_default"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n" />
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.utils.ForceStopRunnable$BroadcastReceiver"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n" />
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxy$BatteryChargingProxy"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.ACTION_POWER_CONNECTED" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.ACTION_POWER_DISCONNECTED" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxy$BatteryNotLowProxy"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BATTERY_OKAY" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BATTERY_LOW" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxy$StorageNotLowProxy"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_LOW" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_OK" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxy$NetworkStateProxy"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.RescheduleReceiver"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.TIME_SET" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.TIMEZONE_CHANGED" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxyUpdateReceiver"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="@bool/enable_system_alarm_service_default"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.UpdateProxies" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.diagnostics.DiagnosticsReceiver"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true"
android:permission="android.permission.DUMP"
android:process=":worker1"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="androidx.work.diagnostics.REQUEST_DIAGNOSTICS" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<!--覆盖官方WorkManager-->
测试场景
- 搜索 widget: AppWidgetSearchToolProvider,是一个广播;下面以搜素 widget 表示搜索 widget 广播
- 搜索 widget 业务 Worker:每隔一个小时的周期性任务;下面以 Worker 表示搜索业务的 Worker
- SystemJobService:API23+ 版本,是 JobService,由
JobScheduler调用;低版本见下面图
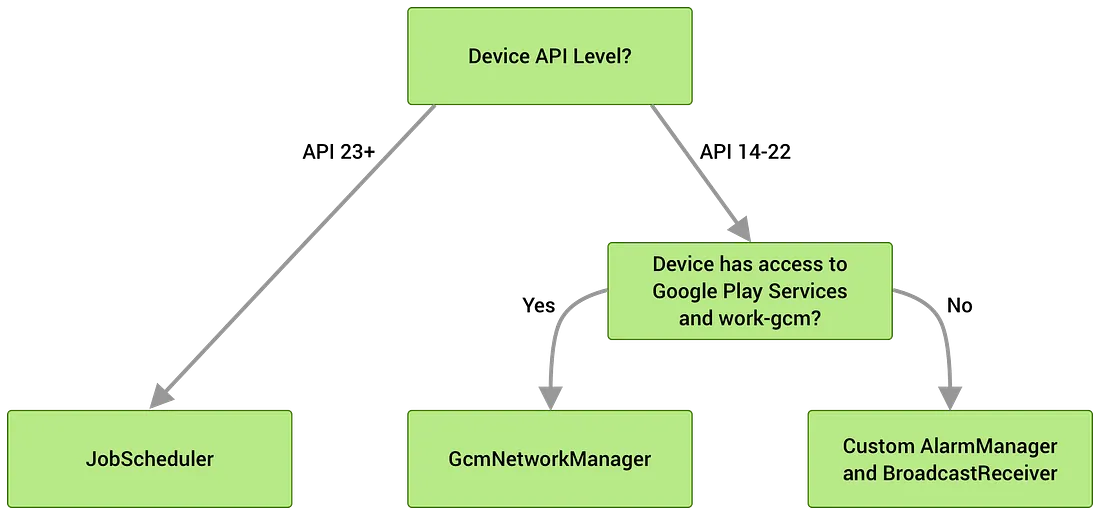
不覆盖 WorkManager SDK 的服务和广播,默认主进程
搜索 widget 在主进程
Worker 不绑定 RemoteWorkerService
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起主进程,AppWidgetSearchToolProvider 是个广播在主进程
# 调用onEnable方法,唤起的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在主进程,添加 widget 时,会调用搜索广播的 onReceiver (
android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起主进程
- WorkManager 周期任务,会唤起主进程
分析:如果主进程存活,直接在主进程执行 Worker;如果主进程不存活,会唤起主进程
Worker 绑定 RemoteWorkerService 在 :worker1 进程
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起主进程,AppWidgetSearchToolProvider 是个广播在主进程
# 唤起主进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在主进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver (
android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起主进程
- WorkManager 周期任务,如果主进程存活不会唤起主进程;主进程不存活,会唤起主进程,随后会唤起
:worker1进程执行 Worker
# 唤起主进程的Intent
SystemJobService
# 唤起:worker1进程的intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a androidx.work.multiprocess.RemoteWorkerService}}
分析: 如果主进程存活,不用唤起主进程;如果主进程不存活,会唤起主进程。主进程唤起后,会唤起
:worker1进程执行 Worker 中的doWork()方法。
搜索 widget 在 :worker1 进程
Worker 不绑定 RemoteWorkerService
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起
:worker1进程
# 唤起worker1进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在
:worker1进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver (android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起:worker1进程
- Worker 周期任务未绑定 RemoteWorkerService,任务在主进程执行,会唤起主进程
# 唤起主进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a androidx.work.impl.background.systemjob.SystemJobService}}
分析:如果主进程存活,直接在主进程执行 Worker;如果主进程不存活,会唤起主进程,执行 Worker 任务
Worker 绑定 RemoteWorkerService 在 :worker1 进程
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起
:worker1进程
# 唤起主进程的intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }
分析:同上
- WorkerManager 周期任务在
:worker1进程,会唤起主进程和:worker1进程
# 唤起主进程的intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{f53cb81 androidx.work.impl.background.systemjob.SystemJobService}}
# 搜索widget唤起的:worker1进程不在时,WorkerManager唤起:worker1进程
待补充
分析: 如果主进程存活,不用唤起主进程;如果主进程不存活,会唤起主进程。主进程唤起后,如果
:worker1进程不存活,会唤起:worker1进程执行 Worker 中的doWork()方法。
Worker 绑定 RemoteWorkerService 在 :worker2 进程
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起
:worker1进程
# 唤起:worker1进程的intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:同上
- WorkerManager 周期任务在
:worker2进程,会唤起主进程和:worker2进程
# 唤起主进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a androidx.work.impl.background.systemjob.SystemJobService}}
# 唤起:worker2进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a androidx.work.multiprocess.RemoteWorkerService}}
覆盖 WorkManager SDK 的服务和广播为 :worker1 进程
搜索 widget 在主进程
Worker 不绑定 RemoteWorkerService
- 添加搜索 widget,会唤起主进程
# 唤起主进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在主进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver (
android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起主进程
SystemJobService会唤起:worker1进程, Worker 运行在:worker1进程
# 唤起:worker1进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a androidx.work.impl.background.systemjob.SystemJobService}}
Worker 绑定 RemoteWorkerService 在 :worker1 进程
- 添加搜索 widget,会唤起主进程
# 唤起主进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在主进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver (
android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起主进程
SystemJobService会唤起:worker1进程, Worker 运行在:worker1进程
# 唤起:worker1进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a androidx.work.impl.background.systemjob.SystemJobService}}
Worker 绑定 RemoteWorkerService 在 :worker2 进程
- 添加搜索 widget,会唤起主进程
# 唤起主进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在主进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver (
android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起主进程
SystemJobService会唤起:worker1进程;Worker 绑定 RemoteWorkerService 运行在:worker2进程
# 唤起:worker1进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a androidx.work.impl.background.systemjob.SystemJobService}}
# 唤起:worker2进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a androidx.work.multiprocess.RemoteWorkerService}}
分析:SystemJobService 注册在
:worker1进程,周期性任务到来时,会先唤起:worker1进程;而 Worker 是绑定到 RemoteWorkerService 的:worker2的进程,所以还会唤起:worker2的进程去执行 Worker 中的doWork()方法
搜索 widget 在 :worker1 进程
Worker 不绑定 RemoteWorkerService
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起
:worker1进程
# 唤起:worker1进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在
:worker1进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver (android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起:worker1进程
- WorkManager 周期性任务,如果到来时
:worker1进程存活则不创建;如果不存活,则创建:worker1进程
Worker 绑定 RemoteWorkerService 在 :worker1 进程
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起
:worker1进程
# 唤起:worker1进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在
:worker1进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver (android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起:worker1进程
- WorkManager 周期性任务,如果到来时
:worker1进程存活则不创建;如果不存活,则创建:worker1进程
Worker 绑定 RemoteWorkerService 在 :worker2 进程
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起
:worker1进程
# 唤起:worker1进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在
:worker1进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver (android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起:worker1进程
- WorkManager 周期性任务,如果到来时
:worker1进程存活则不创建;如果不存活,则创建:worker1进程。Worker 是绑定在:worker2进程,所以还会创建:worker2进程
# 如果:worker1进程不存活,会创建进程:worker1进程
SystemJobService
# 唤起:worker2进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a androidx.work.multiprocess.RemoteWorkerService}}
Worker 绑定 RemoteWorkerService3 在 :worker3 进程
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起
:worker1进程
# 唤起:worker1进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在
:worker1进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver(android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起:worker1进程
- WorkManager 周期性任务,如果到来时
:worker1进程存活则不创建;如果不存活,则创建:worker1进程。Worker 是绑定在:worker3进程,所以还会创建:worker3进程
# 如果:worker1进程不存活,会创建进程:worker1进程
SystemJobService
# 唤起:worker3进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.location.RemoteWorkerService3}}
Worker 绑定 MainRemoteWorkerService4 在 main 进程
class MainRemoteWorkerService : RemoteWorkerService()
<service
android:name="me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.base.MainRemoteWorkerService"
android:exported="false"
android:process="ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets" />
- 添加搜索 widget 会唤起
:worker1进程
# 唤起:worker1进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=3, mIntent=Intent { act=android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED flg=0x10000010 cmp=ai.me.hacket.AppWidgets/me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider }, mInfo=ActivityInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider}}
分析:搜索 widget 的广播注册在
:worker1进程,添加 widget 时,会调用广播的 onReceiver (android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED),这时会唤起:worker1进程
- WorkManager 周期性任务,如果到来时
:worker1进程存活则不创建;如果不存活,则创建:worker1进程。Worker 是绑定在main进程,所以还会绑定 MainRemoteWorkerService 时创建main进程
# 如果:worker1进程不存活,会创建进程:worker1进程
SystemJobService
# 唤起:worker3进程的Intent
appIntent=LinkerIntent{mType=2, mIntent=null, mInfo=ServiceInfo{7c99c5a me.hacket.sample.appwidget.si.base.MainRemoteWorkerService}}
结论
- 添加 widget 会唤起 widget 广播所注册在的进程;widget
onUpdate()方法执行也会唤起进程 - 默认的
SystemJobService和Worker运行在主进程;官方的 WorkManager 多进程方案,是通过绑定到RemoteWorkerService实现 Worker 运行在指定的进程 - 指定
Worker运行所在进程,是通过 bindService 到RemoteWorkerService所在进程运行;SystemJobService默认注册在主进程,还是会被JobScheduler给唤起主进程 - 指定 widget 广播,SystemJobService 和 Worker 到同一个非主进程 (如
:worker1),可以保证不会唤起主进程,只会唤起:worker1进程 - 如果
SystemJobService指定了一个进程,那么项目中其它使用 WorkerManager 的地方的 Worker,都运行在该进程中;如果其它 WorkManager 使用场景想运行到主进程,需要通过RemoteWorkerService指定到主进程 - 低版本 (Android23 一下) 未做测试,未能保证进程唤起行为是否一致
- 未做多种设备的测试,未能保证唤起行为是否一致
方案
所有涉及到的广播/服务都运行在指定进程,如 :widget
方案实施
- 搜索 widget 的广播,指定运行进程为
:widget
<receiver
android:name=".appwidget.si.searchtool.AppWidgetSearchToolProvider"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE" />
<action android:name="com.zzkko.appwidget.CLICK" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.appwidget.provider"
android:resource="@xml/appwidget_info_search_tool" />
</receiver>
- WorkManager SDK 自带的服务和广播,指定运行进程为
:widget
<!--覆盖官方WorkManager-->
<service
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.SystemAlarmService"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="@bool/enable_system_alarm_service_default"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget"
tools:targetApi="n" />
<service
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemjob.SystemJobService"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="@bool/enable_system_job_service_default"
android:exported="true"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_JOB_SERVICE"
android:process=":WIDGET "
tools:targetApi="n" />
<service
android:name="androidx.work.impl.foreground.SystemForegroundService"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="@bool/enable_system_foreground_service_default"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget"
tools:targetApi="n" />
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.utils.ForceStopRunnable$BroadcastReceiver"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget "
tools:targetApi="n" />
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxy$BatteryChargingProxy"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.ACTION_POWER_CONNECTED" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.ACTION_POWER_DISCONNECTED" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxy$BatteryNotLowProxy"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BATTERY_OKAY" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BATTERY_LOW" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxy$StorageNotLowProxy"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_LOW" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_OK" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxy$NetworkStateProxy"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.RescheduleReceiver"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.TIME_SET" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.TIMEZONE_CHANGED" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxyUpdateReceiver"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="@bool/enable_system_alarm_service_default"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":widget"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.UpdateProxies" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.diagnostics.DiagnosticsReceiver"
android:directBootAware="false"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true"
android:permission="android.permission.DUMP"
android:process=":widget"
tools:targetApi="n">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="androidx.work.diagnostics.REQUEST_DIAGNOSTICS" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<!--覆盖官方WorkManager-->
- Worker 运行在指定进程
:widget
使用默认的 CoroutineWorker/Worker 即可
WorkManager 源码修改
Logger前缀默认是VM-,可改成自定义的,避免和系统的 WorkManager 混淆WorkManager默认的数据库为:androidx.work.workdb,可修改WorkDatabasePathHelper.WORK_DATABASE_NAME为androidx.work.workdb.multiprocessPreferenceUtils的PREFERENCES_FILE_NAME改下
Worker 运行到主进程
由于 SystemJobService 指定到了 :widget 进程,默认的 Worker 都是跑在 :widget 进程;如果有需要运行在主进程的 Worker,则需要绑定 RemoteWorkerService 到主进程,具体见下面:
- 定义 MainRemoteWorkerService
class MainRemoteWorkerService : RemoteWorkerService()
- 声明 MainRemoteWorkerService 为主进程
<service
android:name=".appwidget.si.base.MainRemoteWorkerService"
android:exported="false"
android:process="com.zzkko" />
- 安排任务
inline fun <reified W : ListenableWorker> enqueuePeriodicallyWidgetWorker(
context: Context?,
workerName: String?,
repeatInterval: Long = 24,
initDelayMillis: Long = 0L,
isMultiProcess: Boolean = false,
): Operation? {
if (context == null || workerName.isNullOrBlank()) {
return null
}
val requestBuilder = if (!WidgetConstants.isDebug) {
// For release builds, we want to run the worker every 24 hours.
PeriodicWorkRequestBuilder<W>(
repeatInterval = repeatInterval,
repeatIntervalTimeUnit = TimeUnit.HOURS
)
} else {
// For debug builds, we want to run the worker every 15minute to speed up testing.
PeriodicWorkRequestBuilder<W>(
repeatInterval = PeriodicWorkRequest.MIN_PERIODIC_INTERVAL_MILLIS, // WorkManager最低要求是15分钟
repeatIntervalTimeUnit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
)
}
// ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME and ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME are used to determine the service
// that a Worker binds to. By specifying these parameters, we can designate the process a
// Worker runs in.
val builder = Data.Builder().putString(WidgetConstants.WORKER_NAME, workerName)
if (isMultiProcess) {
builder.putString(
RemoteListenableWorker.ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME,
context.packageName
)
builder.putString(
RemoteListenableWorker.ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME,
MainRemoteWorkerService::class.java.name
)
}
val inputData: Data = builder.build()
val workRequest = requestBuilder
.addTag(workerName)
.setInitialDelay(initDelayMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) // 延迟会,先加载本地缓存的数据
.setInputData(inputData)
.setConstraints(Constraints.NONE)
.setBackoffCriteria(
BackoffPolicy.LINEAR,
OneTimeWorkRequest.MIN_BACKOFF_MILLIS,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
)
.build()
val uuid = workRequest.id
L.v(
"enqueuePeriodicallyWidgetWorker() workerName=$workerName(uuid=$uuid), ${if (WidgetConstants.isDebug) "every 15 minutes" else "every 24 hours"}"
)
return WorkManager.getInstance(context)
.enqueueUniquePeriodicWork(
workerName,
ExistingPeriodicWorkPolicy.REPLACE,
workRequest
)
}
问题
ClassCastException
目前 app 存在两套 WorkManager
- WorkManager 指的是官方的 WorkManager SDK,运行在主进程
SiWorkManager引入源码维护的 WorkManager,运行在 : widgetProvider 子进程
问题
主进程和:widgetProvider 进程,同时存在周期性任务(PeriodicWork),Worker 执行不成功,具体报错如下
- 主进程的的周期任务,执行了
:widgetProvider进程的 Worker
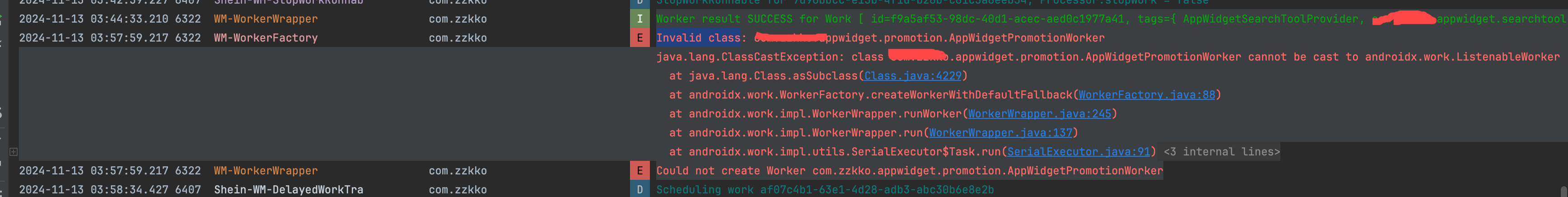
:widgetProvider进程的周期任务,执行了主进程的 Worker
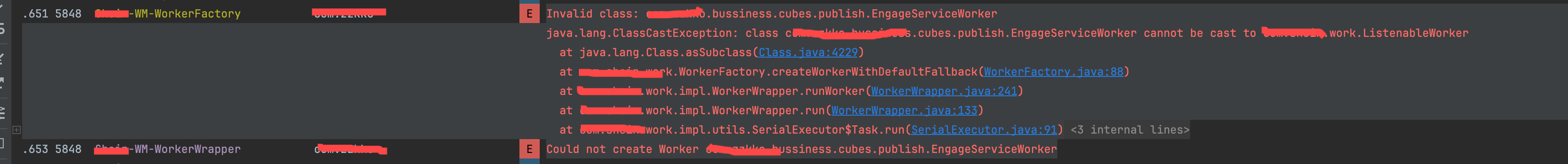
原因
WorkManager 用的官方的,默认在主进程,数据库名为 androidx.work.workdb;而 SiWorkManager 也是这个数据库名,Worker 任务的信息状态都保存在该数据库中
public class WorkDatabasePathHelper {
// ...
private static final String WORK_DATABASE_NAME = "androidx.work.workdb";
// ...
}
当同时存在 WorkManager 和 SiWorkManager 的周期性任务。
以主进程为例:
主进程的 SystemJobService 周期任务到来时,从 androidx.work.workdb 的 WorkSpec 读取到 Enqueued 状态的 Worker,执行 Worker,先通过 WorkFactory 创建 Worker,创建不成功然后会反射创建 Worker,是从 WorkSpec 表中的字段 worker_class_name 记录的类的全路径来进行反射的,由于官方的 WorkManager 默认反射创建的是 androidx.work.ListenableWorker,而 SiWorkManager 的 Worker 是 继承的com.shein.work.Worker,导致 ClassCastException
:widgetProvider 进程存在类似问题。
为什么首次安排能执行成功,第 2 次就出现失败?
分析
根据任务的 Constraint,不同系统选择的 Scheduler 不一样,大致分为
- GreedyScheduler unconstrained, non-timed work
- SystemJobScheduler Android23 及 +
- GcmScheduler Android23 以下,如果存在
- SystemAlarmScheduler Android23 以下
整个调用过程链路很长,最终创建 ListenableWorker 对象是通过工厂 WorkerFactory 来创建的,封装了 createWorkerWithDefaultFallback 方法来创建
public final @Nullable ListenableWorker createWorkerWithDefaultFallback(
@NonNull Context appContext,
@NonNull String workerClassName,
@NonNull WorkerParameters workerParameters) {
ListenableWorker worker = createWorker(appContext, workerClassName, workerParameters);
if (worker == null) {
// Fallback to reflection
Class<? extends ListenableWorker> clazz = null;
try {
clazz = Class.forName(workerClassName).asSubclass(ListenableWorker.class);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
Logger.get().error(TAG, "Invalid class: " + workerClassName, throwable);
}
if (clazz != null) {
try {
Constructor<? extends ListenableWorker> constructor =
clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Context.class, WorkerParameters.class);
worker = constructor.newInstance(
appContext,
workerParameters);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Logger.get().error(TAG, "Could not instantiate " + workerClassName, e);
}
}
}
if (worker != null && worker.isUsed()) {
String factoryName = this.getClass().getName();
String message = String.format("WorkerFactory (%s) returned an instance of a "
+ "ListenableWorker (%s) which has already been invoked. "
+ "createWorker() must always return a new instance of a "
+ "ListenableWorker.",
factoryName, workerClassName);
throw new IllegalStateException(message);
}
return worker;
}
大体逻辑是先调用 createWorker 来创建;由于我们未提供自定义的 WorkerFactory,这里返回 null;
返回 null 就会通过反射来创建:
clazz = Class.forName(workerClassName).asSubclass(ListenableWorker.class);
workerClassName 是从数据库 androidx.work.workdb 的 WorkSpec 表中的 worker_class_name 字段读取的
// WorkerWrapper.java
mWorkSpec = mWorkSpecDao.getWorkSpec(mWorkSpecId);
// WorkSpecDao.java
@Query("SELECT * FROM workspec WHERE id=:id")
WorkSpec getWorkSpec(String id);
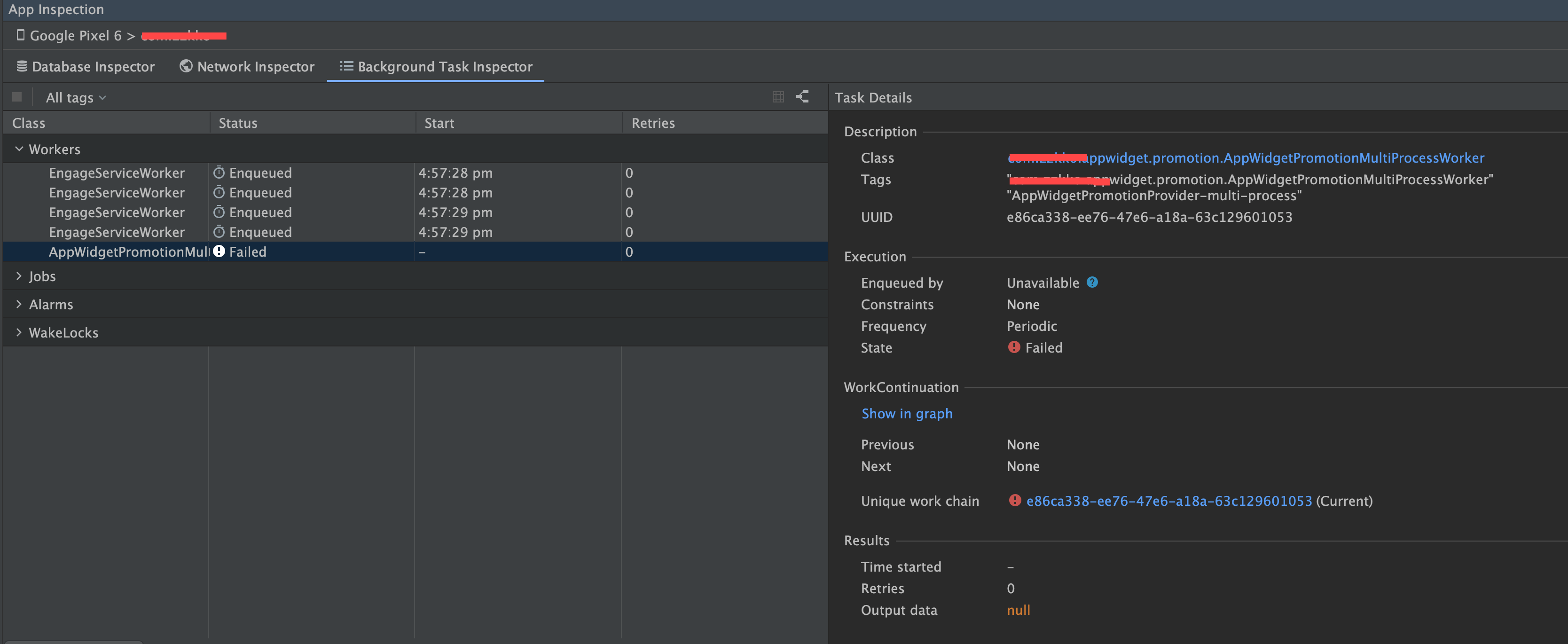
由于主进程和:widgetProvider 进程共用数据库,就会异常情况:
- 主进程读取到了: widgetProvider 进程的 worker 任务
- : widgetProvider 进程读取到了主进程的 worker 任务
:widgetProvider 进程的 ListenableWorker 是我们内部自己维护的,包名和官方的不一致,在进行反射的时候,就会抛出 ClassCastException 异常,导致 Worker 任务失败
解决
- 自定义 WorkFactory
主进程和子进程还是共享数据库,不推荐
- 主进程和子进程数据库区分开: 将主进程和: widgetProvider 进程在不同的数据库中,主进程和: widgetProvider 进程的数据库隔离开,这样就不会读取到非自己进程的 woker 任务
- 主进程的数据库不变
- : widgetProvider 进程(自己内部维护的 SiWorkManager)的数据库名改成
androidx.work.workdb.multipprocess
// 修改后,基于v2.7.1
public class WorkDatabasePathHelper {
// ...
private static final String WORK_DATABASE_NAME = "androidx.work.workdb.multipprocess";
// ...
}
FAQ?
一个 WorkManager 在主进程,一个在子进程?
可以的。
需要在子进程运行的 Worker 需要单独改造;在主进程的 Worker 不用做什么特殊处理。
多进程参数传递
private fun buildOneTimeWorkRemoteWorkRequest(
componentName: ComponentName, listenableWorkerClass: Class<out ListenableWorker>
): OneTimeWorkRequest {
// ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME and ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME are used to determine the service
// that a Worker binds to. By specifying these parameters, we can designate the process a
// Worker runs in.
val data: Data = Data.Builder()
.putString(RemoteListenableWorker.ARGUMENT_PACKAGE_NAME, componentName.packageName)
.putString(RemoteListenableWorker.ARGUMENT_CLASS_NAME, componentName.className)
.build()
return OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(listenableWorkerClass)
.setInputData(data)
.build()
}
// 调用
val serviceName = RemoteWorkerService::class.java.name
val pkg = "${applicationContext.packageName}:work1"
val componentName = ComponentName(pkg, serviceName)
val oneTimeWorkRequest = buildOneTimeWorkRemoteWorkRequest(
componentName,
ExampleRemoteCoroutineWorker::class.java
)
pkg 子进程还是当前 packageName,如果是子进程,报错
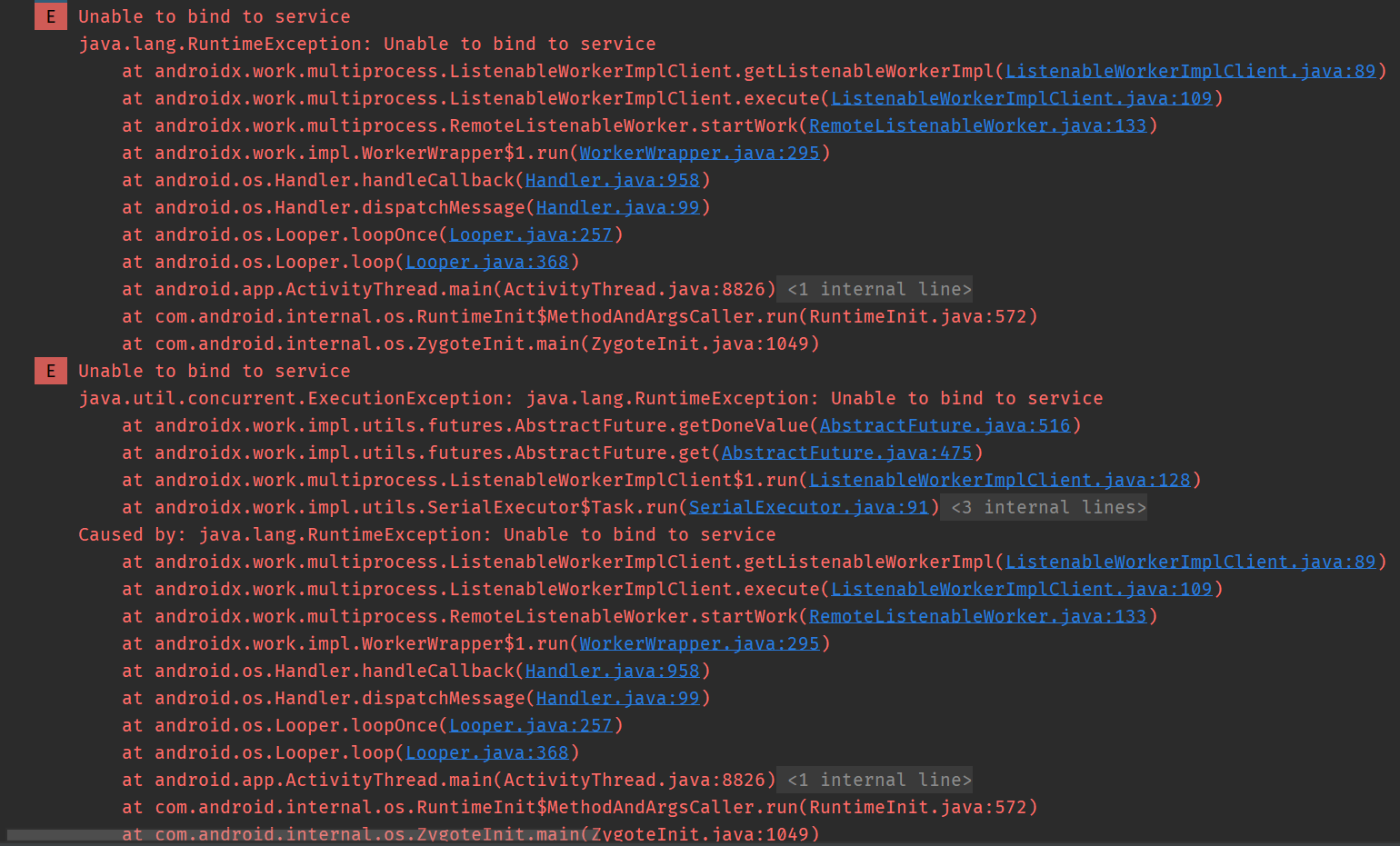
正确的是
applicationContext.packageName